DC leakage and DC withstand voltage test purpose and principle
For good insulation, the leakage current under the direct voltage is very small. At the same time, under the same direct voltage, the current through the insulation is subject to pressure.
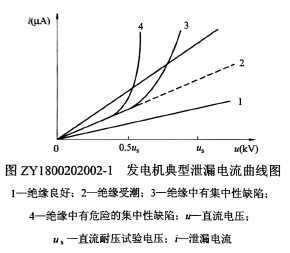
Fig. ZY1800202002-1 shows the measured leakage current of the generator. It can be seen from figure ZY1800202002-1 that it is good
Insulation, with the increase of the applied DC voltage, the leakage current increases due to the accelerated ion movement speed, but in the not too high voltage range,
The leakage current is linear with the increase of the applied voltage, and the rise is small.
As shown in curve 1 of figure ZY1800202002-1; after the insulation is wet, the leakage current increases greatly with the applied voltage.
When there is a concentrated defect in the insulation shown in curve 2 of figure ZY1800202002-l, leakage occurs when the applied voltage rises to a certain value.
The increase in current flow, as shown in curve 3 of Figure ZY1800202002-l, the more severe the concentration of insulation defects, the lower the voltage at which the leakage current surge point will appear, as shown by curve 4 in Figure ZY1800202002-1. Leakage current test refers to the application of different values ​​of DC voltage to the insulation within a certain range of DC test voltage, and measuring the corresponding leakage current through the insulation, by the size of the current and the curve of the relationship between current and voltage, it is possible to analyze and judge the insulation Performance. From the above, it is known that the principle of the leakage current test is consistent with the insulation resistance test. However, the leakage current test has the following advantages over the insulation resistance and absorption ratio tests.
(1) The DC test voltage used in the leakage current test is supplied by the high-voltage rectifier equipment. The voltage value is higher than that of the insulation resistance meter and can be adjusted. For a certain voltage level of equipment insulation can be applied to the corresponding test voltage, so that the weakness of the insulation itself is more easily displayed.
(2) Leakage current test is to use micro-ampere meter to indicate the leakage current value, high sensitivity and accurate reading than insulation resistance meter.
(3) The insulation resistance value can be converted according to the measured value of the leakage current, and the insulation resistance value measured by the insulation resistance meter cannot generally calculate the leakage current value. This is because according to the load characteristics of the insulation resistance meter, the terminal voltage output from the insulation resistance meter is related to the size of the insulation value of the test object, and it is not necessarily the standard voltage of the insulation resistance meter nameplate.
(4) Leakage current test The relationship between the leakage current and the pressurization time and the relationship between the leakage current and the applied voltage can be plotted, and the insulation status can be judged by these curves.
In summary, the leakage current test is more sensitive and effective than the insulation resistance test for finding insulation defects. The DC voltage withstand test is to apply a DC test voltage higher than its rated working voltage to the insulation of the electrical equipment for a certain period of time, and to observe whether insulation breakdown or other abnormal conditions occur. The principle, wiring, and method of the DC voltage withstand test and the leakage current test are the same. But the role of the two is different, DC voltage
The test is to test the dielectric strength of the insulation, and the test voltage is higher. The DC leakage current test is to check the insulation condition and the test voltage is low. Therefore, the DC voltage withstand test is more meaningful for the detection of certain local defects.
Water Treatment
The main objectives of water treatment are:
1. Removal of suspended solids: This is
usually done through processes like sedimentation and filtration to remove
particles, dirt, and other suspended matter from the water.
2. Disinfection: Water treatment also
involves disinfection to kill or inactivate harmful microorganisms such as
bacteria, viruses, and parasites. Common disinfection methods include
chlorination, ultraviolet (UV) radiation, and ozonation.
3. Removal of dissolved impurities: Many
water sources contain dissolved impurities like minerals, salts, and organic
compounds. These impurities can affect the taste, odor, and overall quality of
water. Processes like ion exchange, reverse osmosis, and activated carbon
filtration are used to remove these dissolved impurities.
4. pH adjustment: The pH level of water can
impact its corrosiveness and taste. Water treatment may involve adjusting the
pH level through the addition of chemicals to make it more suitable for its
intended use.
5. Removal of specific contaminants: Water
treatment can also target specific contaminants that may be present in the
water, such as heavy metals, pesticides, and industrial pollutants. Advanced
treatment technologies like adsorption, chemical precipitation, and membrane
filtration are used for this purpose.
Overall, water treatment plays a crucial
role in ensuring the safety and quality of water for drinking, industrial
processes, agriculture, and environmental protection. It helps to prevent
waterborne diseases, maintain public health, and conserve water resources.
RO Antiscalant Water Treatment, Silicon-Phosphorus Crystal for Water Treatment
Sichuan Jinhe Qihang Co,. Ltd. , https://www.jinhechemicals.com