Finite Element Analysis and System Design of Forklift Gantry

Baoji Heli Forklift Factory - Wu Jinggang, Zhang Zhancang
Chang'an University - Ma Pengfei
Abstract: This paper presents a finite element analysis approach to evaluate the structural behavior of a forklift gantry. A simplified model was developed, and an associated software system was designed to support the analysis and design process. The study provides a practical method for analyzing forklift structures and can be referenced in the design of other engineering machinery. The methodology emphasizes the importance of understanding the overall structural behavior rather than focusing solely on key load points.
Keywords: Finite element analysis; Forklift gantry; Structural design; Engineering software; Stress distribution; Load simulation.
1. Calculation Model of Forklift Frame Structure
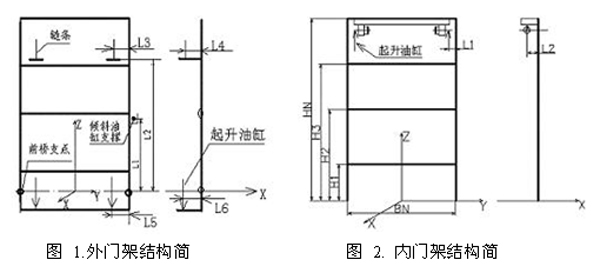
The connection between the inner and outer gantry of the forklift is achieved using rollers embedded in channel steel. The number of beams varies depending on the maximum lifting height, with a minimum of 2 and a maximum of 4 for the inner gantry, while the outer gantry can have up to 5 beams. When the gantry is lifted, the hoist lifts the inner structure, enabling the fork to raise the load. The swinging motion of the outer gantry is controlled by a tilting cylinder, with the front axle acting as the pivot point, allowing a swing range of up to 12 degrees.
For easier calculation and analysis, the gantry structure was simplified. The internal and external dimensions and configurations are illustrated in Figures 1 and 2. Based on the structural layout, movement patterns, and loading conditions, a space beam element was used for the finite element analysis.
2. Stiffness Matrix and Coordinate Transformation
2.1 Node Displacement and Node Force
For a space beam element, the node displacement and nodal forces are shown in Figure 3. The displacement matrix at the i-node is represented as follows:
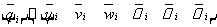
Similarly, the j-node displacement matrix is given by:
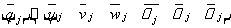
The combined displacement matrix for the unit is:

The force matrices at the i-node and j-node are:
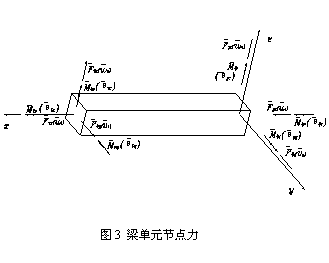
The complete node force matrix is:
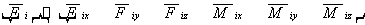
The j-node force matrix is:
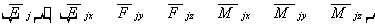
And the final node force matrix is:
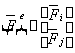
2.2 Element Stiffness Matrix and Stiffness Equation
The stiffness equation for the element is given by:
Where  represents the element stiffness matrix, and
represents the element stiffness matrix, and 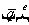 denotes the nodal displacements. The stiffness matrix is divided into four sub-matrices, resulting in a 12x12 matrix due to the 12 degrees of freedom in a space beam element.
denotes the nodal displacements. The stiffness matrix is divided into four sub-matrices, resulting in a 12x12 matrix due to the 12 degrees of freedom in a space beam element.
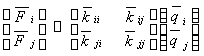
The structure is divided into nodes based on beam elements, followed by load processing, stiffness matrix computation, global stiffness matrix assembly, displacement calculation, and end force evaluation. The program was developed using Visual Basic (VB) to allow direct visualization of results such as displacement, stress, and internal forces.
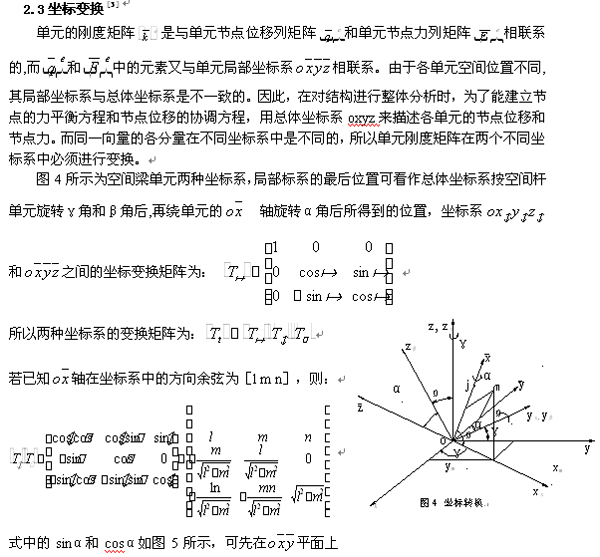
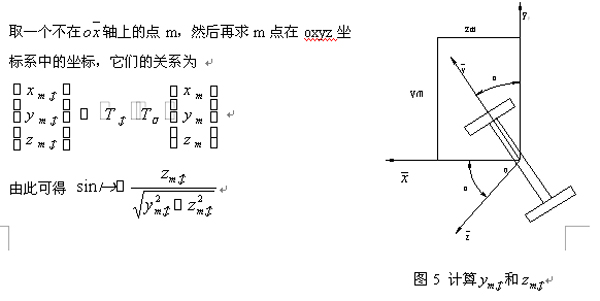

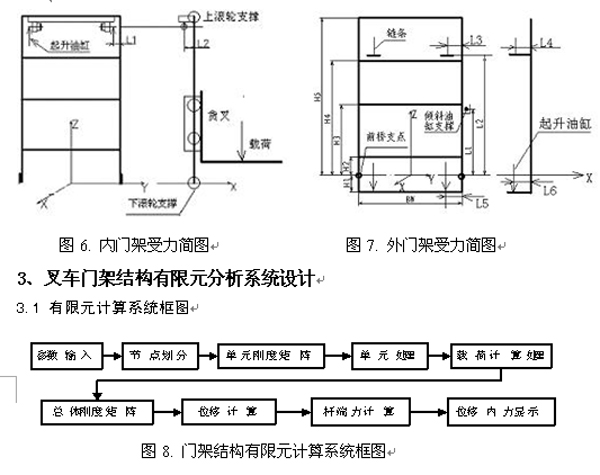
4. Design of Finite Element Calculation Software System
The software system consists of three main components: parameter input, node division, and result display. Parameter input includes load, structural, and material properties. Channel steel is used for columns, and A3 steel for beams with rectangular cross-sections. The system incorporates a material database to store relevant parameters for channel steel. Users can select the appropriate model and input section dimensions for the beams.
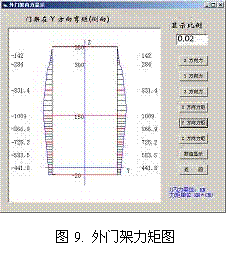
The background processes, including node partitioning and finite element calculation, are complex, but the user interface is kept simple. The core of the system lies in the underlying program that performs the calculations. Results are displayed in two formats: graphical and numerical. The graphical display uses Picturebox controls to plot internal force diagrams, such as the bending moment diagram of the outer frame, as shown in Figure 12. Numerical data is retrieved from generated text files using the RichTextBox control in VB.
5. Conclusion
Through the analysis of the forklift frame, a computational model was established, and coordinate transformation under spatial coordinates was addressed. Based on this, a finite element analysis and calculation system was developed for the forklift gantry. This system provides an effective and practical tool for evaluating and designing forklift structures, offering valuable insights for future engineering applications.
References:
[1] Liu Jiqing, "Structural Mechanics", National Defense Industry Press, April 1985, Beijing.
[2] Lei Xiaoyan, "Finite Element Method", China Railway Publishing House, October 2000.
[3] Liu Erlie, "Finite Element Method and Programming", Tianjin University Press, July 1999.
[4] Qingyuan Computer Studio, "Visual Basic 6.0 Development Guide", Machinery Industry Press, April 1999.
Glass And Window Film,Glass Pe Protective Film,Waterproof Window Glass Pe Film,Window Glass Film
Wuxi Xinhao Protective Film CO.,Ltd , https://www.cotton-balewrap.com